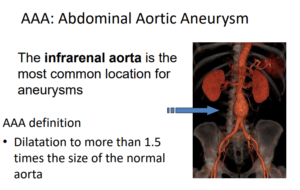
What is Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm?
“When we talk about Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Treatment, try to picture the lower part of your aorta getting bigger and bigger. It if grows too much, then the risk of a rupture increases, and the level of danger is higher.
Your life could be in danger and measures need to be taken.
Professional measures in this case, as in any medical case.
An aneurysm takes place when plaques build up inside artery walls. With age these plaques appear more often, affecting the levels of oxygenated blood that are transported to every single part of your body.
Signs and Symptoms
An aneurysm can grow at a very slow rate, without showing any signs over time. Most are spotted on a checkout with your trusted health professional.
If there is a problem, then you will experience any or several these symptoms:
- A sharp pain in your chest, abdomen or lower back. This uncomfortable sensation can lasts several hours or days. The pain could span through buttocks or legs.
- A toe turns black or, maybe, blue.
- You notice your skin is kind of sweaty
- You start to feel dizzy or weak
- Your heart rate increases dramatically
- Vomit
Diagnosis
As in everything related with health, the sooner a diagnosis is done, the better.
The Vascular Group of Naples is an institution that advocates for the use of the best technology available.
These are some of the terms you will find more often:
- Angiogram: this is the most used term in the field when it comes to diagnose an aneurysm. During an X-Ray procedure, blood clots are exposed thanks to a catheter.
- Abdominal Ultrasound: This procedure allows the physician to have a clear “picture”, thanks to sound waves that go through body tissue located in the abdomen.
- CT Scan: Here, a bigger picture is taken, in the sense that images are created not only of the abdomen, as with the Abdominal Ultrasound, but the aorta, heart and blood vessels.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This is a big piece of equipment, a magnet to be more precise. Computerized images of heart and vessels are created in a very detailed way.
Causes
Most of the causes are related with one thing: your lifestyle.
To be more specific, you avoid it by having a healthy lifestyle.
Chances of suffering an Aneurysm are higher if you are overweight, if your diet includes foods with high presence of fat or if you smoke on a regular basis.
There are also other causes that are not under your control like infections on the aorta or high blood pressure.
Risk Factors
Other risk factors that are out of your control are:
- If you are over 65 years old.
- Men have a higher propensity to suffer an abdominal aneurysm.
- Genes play a role here as well, if there is history in your family, there are a chances of having an aneurysm at a younger age.
Prevention
Even there are some factors that you cannot control directly, there are activities that can help you prevent an aneurysm, and most diseases, just by using a daily discipline:
- Heart health: stay away from cigarettes. In general, avoid smoking.
- Medication: if you have being diagnosed and are require taking your medication, try to follow your physician instructions as much as you can.
- Screening test: to be more certain, scheduled an ultrasound with your physician. It helps to spot any kind of problem right away.
Initial Management
Going into more detail, if you are diagnose, this is an overview of how the procedure will be:
– Prehospital care
As with any health procedure, paying attention to details is critical.
You can visualize prehospital care as follows:
- Breathing is highly important, that is why our professionals makes sure that you don´t have any problem by maintaining a proper oxygenation all the time.
- The physician in charge may ask some question to know more about the history of the patient.
- As in any hospital procedure, the patient vital signs will be monitored upon arrival or while on route to the hospital in an ambulance.
- The physician must pay attention to any symptom that might indicate that the patient could suffer a shock during the intervention.
– Emergency department care
When conditions mandate that the patient needs surgical intervention, all the equipment and procedures are set up to deal with things like: hemorrhagic shock, which are dealt with blood transfusions and surgery.
The clinicians must be aware of sudden changes in blood pressure.
Options for Surgical Intervention
Over the last 50 years there have been 2 established procedures:
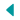
– Open Repair
Open repair of AAA has a survival rate of 96%. Cardiac risk is reduced thanks to constant cardiac investigations and beta blockade.
Laboratory assessment is one of the first steps that need to be performed as well as a careful examination of the patient history and amplification on some details the clinician might consider of high importance.
Patient current lifestyle needs to be carefully examined to spot possible mental and physical deterioration.
All risk factors are listed and taken in consideration.
– Endovascular Repair
Also known as EVAR, has become, over the last 30 years, into a wide alternative to Open Repair.
Its minimal invasive techniques and lower preoperative risks made this one of the most used procedures. It has extended, even to elder population.
EVAR consist in accessing the abdominal aorta via small incisions over the femoral vessels.
An endograft is placed within the lumen of the AAA.
Think of these grafts as protection that decreases the pressure of the walls. This way, the risk of aortic rupture is lowered.
Consultations
The support of a radiologist is mandatory to determine if ultrasonography or Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
If the abdominal aorta exceeds a diameter of 3 cm there must be a follow-up with a vascular surgeon.
Over 4 cm a surgical repair is the best approach.
As in any surgery, anesthesia is required along with the necessary personnel to perform a successful surgery.
All professional health assessment needs to be done with precision and quality standards must be followed.
Complications
If it is too late and the AAA is not diagnosed, these problems may arise:
- Rupture: there is only a 20% survival rate in an emergency situation. Remember that the aorta supplies most of the blood to the body. That´s why is so critical.
- Blood clots: that bloods flows through the body without any restriction is vital. That´s why a block on any blood vessel can cause troubles.
Aneurysm Terminology
Aneurysm Definition: for adult patients, a diameter bigger than 3 cm, is considered aneurysmal.
Less than 4.0 cm, we talk about small aneurysms.
Between 4.0 cm and 5.5 cm we talk about medium aneurysms.
Larger than 5.5 cm, are called larger aneurysms.
An expansion larger than 5.0 cm in a period of 6 months increases the risks.
Aneurysm Repair
Elective AAA repair is not recommended until the risk of rupture exceeds the risks associated with repair. This is a critical point where professional decisions are needed.
Other factors are very important to be considered: the presence of a coexistent peripheral artery disease. Diseases such as: iliac aneurysm and femoral aneurysm.
Observations are key when talking about conservative management. These procedures include clinical evaluation and AAA surveillance
Medical Risk Assessment
As physicians, we look for perioperative complications such as: coronary ischemia, arrhythmias or pneumonia.
Patients with smoking history need a closer observation, since the risk factors are more much higher and there are correlated with other diseases.
Conservative Management
As an accepted rule, AAA smaller than 5.5 cm need to be managed in a more conservative way.
Potentially Beneficial Therapies:
- Stop smoking: aneurysm is a word with high chances of being mentioned on a regular smoker record.
It is on the patient´s will and discipline to control this behavior. More than control it, it is best to eliminate it definitely.
- Physical activity: a daily physical activity is a must for patients diagnose with AAA, this a fact accepted not only in the medical community but in society in general.
Moderated physical activity is the first step. It is best if these activities are monitored by a health professional. Otherwise, the risks will be others. Moderation is best.
Professional recommendation also applies for a proper diet.
Statistics
In the paper “Epidemiology of Aortic Aneurysm Repair in the United States from 1993 to 2003”, it is stated that AAA has been described in the medical community over the last 50 years.
To spot trends in mortality, samples were taken between 1993 and 2003 in the United States.
These are their results:
“Overall rates of treated unruptured and ruptured AAAs remained stable (unruptured 12 to 15/100,000; ruptured 1 to 3/100,000). In 2003, 42.7% of unruptured and 8.8% of ruptured AAAs were repaired through an endovascular approach. Inhospital mortality following unruptured AAA repair continues to decline for open repair (5.3% to 4.7%, P = 0.007).
Mortality after elective endovascular AAA repair also has statistically decreased (2.1% to 1.0%, P =0.024) and remains lower than open repair.
Mortality rates for ruptured AAAs following repair remain high (open: 46.5% to 40.7%, P = 0.01; endovascular: 40.0% to 35.3%, P =0.823).”
This shows certain level of stability for patients treated with elective is Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, although there is a change in the treatment paradigm where there is a preference for elective endovascular AAA repair.